Animal-like Protists Are Characterized by Which of the Following
Animal-like Protists Are Characterized by Which of the Following
- Protists Facts and Types - Animate being Similar, Plant Like, Mucus Like
For most individuals, the showtime images seen through the lens of a microscope are protists -- unicellular organisms that don't possess enough characteristics to be divers as purely plant or animate being.
The organisms within the Kingdom Protista incorporate a nucleus, similar all Eukaryotes, and are categorized equally plant-similar, brute-like or fungus-like.
Uncomplicated Images
Protists are abundant in the world effectually us, normally thriving in aqueous environments; they survive in bodies of h2o as well as the human being body.
A sample of pond water or its moist surrounding area placed on a slide under a compound microscope yields images of living organisms such as paramecium and amoeba – inexpensive and piece of cake, this is oft a pupil's introduction to microscopy.
Samples are live, frequently moving and differ with each drib of water; these seemingly unproblematic images provide the ground for identifying structures within a cell – an invaluable foundation for the study of prokaryote and eukaryote specimens.
Kingdom Protista
Protists possess characteristics that make them "similar" multi-cellular organisms, nonetheless they lack certain backdrop to be classified as animate being, establish or fungus. The presence of a nucleus in all protist organisms means they are all eukaryotic.
The three primary classifications in the Protista Kingdom and subsequent phylum include:
Animal-like or Protozoan
- Ciliates (including Planktonic subgroups)
- Flagettes (Zooflagellates)
- Sarcodines (amoebas belong to this group)
- Sporozoans
Establish-like or Diatoms
- Chlorophyta (greenish algae, by and large single cell)
- Rhodophyta (red algae or seaweed, multi-cellular)
Fungus-like
- Decomposers
- Molds (slime molds, mildew)
Many protists overlap in classification, such as lichen – considered a type of algae and mucus and some, like carmine algae, are amidst the few multi-cellular protista organisms.
Literally defined as "the very starting time," Protista are believed to be the start known organisms. Still, it is important to annotation the miscellany nature of this Kingdom, specifically that groups of protista are not related to one another in the same manner as Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes.
Containing over 80 groups and over 115,000 species, the Kingdom Protista represents a wide range of Eukaryotic organisms bound simply by the fact that they human action like animals, plants or fungi.
Nucleus
Eukaryotic organisms possess a nucleus in each prison cell. Whether an organism contains one or multiple cells, the nucleus – the first and largest organelle discovered – is essential to cell life.
Protected in a double envelope, cytoplasm crosses through pores in the outer membrane; this is unlike prokaryotes, where cytoplasm straight crosses the cell wall.
Actualization like a darkened surface area inside the nucleus under a light microscope, the nucleolus is surrounded by chromatin, which contains Deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA – necessary for cell sectionalization.
Serving as a conduit betwixt the pores in the nuclear envelope, the endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for the in/out transport of compounds.
Animate being-similar Protista
Animal-similar protists or protozoan are primarily identified by method of movement such as:
- Pseudopods or "imitation feet" – amoeba and organisms belonging to Sarcondine Phylum have no truthful shape, moving via projections of cytoplasm
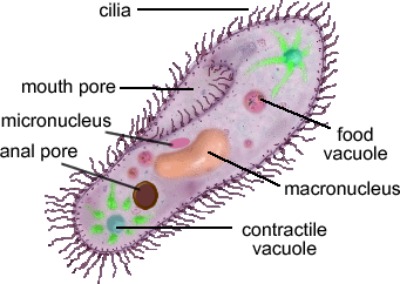
- Cilia – paramecium and plankton from Ciliate Phylum use tiny hairs that line the outside of the cell
- Flagella – from the Phylum Mastigophorans; Euglenoids whip a sole flagellum, Dinoflagettes employ 2 flagella
Ciliates Paramecium from BiologyCorner.com
In add-on, parasitic protists such as sporozoans also fall under animal-similar, only are categorized past the way they survive and diseases brought about in hosts.
Animal-similar protozoan are also heterotrophic and contain organelles such as a jail cell membrane and food vacuole.
Institute-Like
Considered the foundation of many aquatic food chains, responsible for over forty percent of photosynthesis that occurs in salt and fresh bodies of water, as well equally essential to the production of oxygen in the atmosphere, constitute-similar protista are classified into three phylum:
- Euglenophytes – one-celled Euglena are located in fresh water and contain chloroplasts; they possess found and animal traits, functioning autotrophic when lite and heterotrophic when dark
- Chrysophytes – comprise chlorophyll and are autotrophic through photosynthesis; examples include:
- Diatoms
- Light-green Algae – can live in fresh or salt water and sometimes moist land; many, like Volvox, form colonies
- Cherry-red Algae (seaweed) – multi-cellular, live in deep salt water; in uncontrolled spurts, this algae has been responsible for ecological damages
- Brown Algae – type of seaweed with large leafs called "blades," contain root and air sac structures; thrive in salt h2o; can grow to heights in backlog of 100 anxiety; appear nigh plant-like of the algae
- Dinoflagelles – contains chlorophyll and uses two flagella to move; creates a porous glass (silicon) shell; sometimes glows in the dark body of water floor
Come across Euglena under the microscope
Although each contains chlorophyll, organisms such as Dinoflagelles have properties that are both brute and constitute like.
This overlap is exclusive to Eukaryotes in the Protista Kingdom.
Mucus-Like
Fungus-similar protists have cells walls like to plants, which contain chitin, but possess the animate being-like role of heterotrophy. They release spores into the air to reproduce and take the ability to movement, although this might only happen once during a lifespan.
Requiring a moist environment to survive, the three types of mucus-like protists are:
- Slime molds – oft seen on decaying establish life or copse, these protists sustain on bacteria and other microorganisms that appear on rotting plants nether wet conditions; the two types, plasmodial and cellular, can appear in a range of colors
- Water molds – live in shallow or damp places; can be every bit decomposer or parasite; every bit a mold, it can be harmful if institute in gardens and farms, detrimental to potatoes, corn and cabbage and tin harm a host as a parasite; looks like a combination of fuzz and threads
- Downey mildews – similar to water molds, downey mildews are harmful to certain vegetable life
Mucus-similar organisms also have instances of overlapping. For example, certain slime molds are the result of stressed amoebas merging into a pseudoplasomodium (slug); this fungal "trunk" is able to relocate and reproduce by releasing spores.
Microscopy
All types of protista organisms can exist studied under a elementary calorie-free microscope and some, like fungus, can be seen with the naked eye.
Microscopy studies tin be as easy as using a pipette to drop swimming water onto a slide and viewing live paramecium as they movement in their natural surroundings.
Advanced techniques such every bit dark field illumination or phase contrast are used to view structures in greater particular. Comparing images from each technique also yields valuable information.
Unicellular Eukaryotes, protists provide a foundation for viewing multi-cellular plants and animals. Oftentimes used in introductory microscope experiments, the showtime image many students see through a lens is an amoeba or paramecium.
Although members of the Kingdom Protista do not contain all the organelles institute in plants and animals, they do contain a well-defined nucleus, providing a foundation for more advanced microscope study.
More on Protists:
Paramecium - Classification, Structure, Function and Characteristics
Acanthamoeba - Life Bike, Morphology and Affliction/Infection
Vorticella - Characteristics, Structure, Reproduction and Habitat
Trichonympha - Definition, Nomenclature and Characteristics
See Too:Ciliates Microscopy, Plankton Microscopy, Algae - Reproduction, Identification and Classification
Have a look at Fungi - Types, Morphology and Construction
Here, learn more than near Cell Civilization , Jail cell Sectionalisation,Cell Differentiation and Cell Staining as well asGram Stain .
Of interest: Further reading here about Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes.
More on Unicellular Organisms - Discussing Protozoa, Bacteria, Fungi, Algae and Archaea Here
Render from Protists to Prison cell Theory
Animal-like Protists Are Characterized by Which of the Following
Source: https://www.microscopemaster.com/protists.html


Komentar
Posting Komentar